I have decided to do a beginners guide to BI on my blog. I thought this would be a great way to tie all the resources I use and give you a good idea for an approach to BI projects. I am starting off with a question that needs to be answered.
What is Business Intelligence About? Decisions of Course
I often find myself in situations where I have to try and explain Business Intelligence. It’s not that easy to define BI in a universal definition that everyone agrees with. BI is as much a collection of technologies and principles as anything else.
So here it goes,
‘Business Intelligence is about taking the guess work out of the decision making process.’
That’s right it’s not about technology or a wonderful new process. It’s about the management decision making process that occurs in every business. To demonstrate this in more detail lets review what the Management Decision Making Process (MDMP) is about.
The MDMP was introduced to me on my first data warehousing project by Peter Nolan the architect of the project. He took me through the concept of why you want to start a BI project in the first place. He posed a simple question, ‘How is Business?’
There are four primary drivers that make up a cycle that form the MDMP. Consider each factor as deliverables forming a BI platform. The diagram below shows four primary drivers for the MDMP.
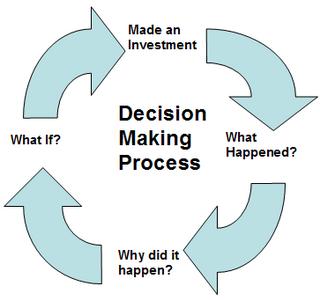
Made an Investment – Every organization makes an investment either in a product or a service. The tracking of the investment is the first driver in the MDMP. For example a product stock keeping or a resource schedule report allows a compony to track its resources.
What Happened? – The second driver covers the result of the investment. Did the investment payoff, did we make a sale? For example a sales report allows business to track the success of the investments.
Why did it happen? – The third driver is to analyse the success of the investment. Organizations use OLAP analysis Ad-hoc reporting to drill down to the reasons for the performance.
What if? – The fourth and final driver and the most difficult to implement. Organizations are constantly looking for new opportunities to invest, questions like; what is the impact of further investment? What if we gave 10% further discount? Looking for new opportunities with data mining and forecasting techniques helps answer this question.
So how do you deliver MDMP?
When starting a BI project you must set firm goals around the end deliverables. A great place to start is taking a single business process and mapping to the MDMP. (Selecting a business process is an entirely different subject for a blog.)
Once a process has been selected a solid business case been derived using the MDMP. The four primary drivers of MDMP will allow you to set clear goals for delivery that the business can understand.
SQL Server 2005 vs. MDMP
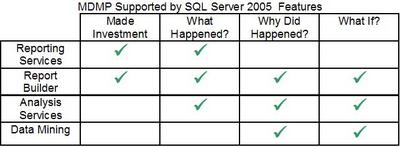
Reviewing the SQL Server 2005 product against MDMP shows how much BI functionality Microsoft has release in the version. Below is a table showing the reporting functionality SQL Server 2005 has built into support the MDMP.
Conclusion
Basing your BI project on the MDMP you have a common point of view across the business and technology requirements are key to delivering a successful project. For further information on the MDMP check out the resources below.
Resources
Getting Started and Finishing Well By Peter Nolan
http://www.intelligententerprise.com/010507/print/webhouse.htm
Where is Peter?
http://www.peternolan.com/
Beginners Guide to Business Intelligence: What is a Data Warehouse?